As a kind of water measuring instrument, water meter occupies a very important position in our daily life. However, when asked, do you know water meter? Maybe most people know very little.
Now, let's learn something about the development of water meters!

Theoretical preparation for the invention of water meter
The emergence of water meter is closely related to the development of modern physics. As early as 1630, the famous physicist Galileo made an experiment to accurately measure time by water flow. In 1644, Italian physicist Torricelli studied the theoretical velocity of water flow, which is the same as that of objects with the same height as the nozzle head falling in vacuum. In 1738, the "Bernoulli equation" determined by Swiss scientist Bernoulli applied the law of energy conversion and conservation to the analysis of water flow. By the end of the 18th century, the formula of the relationship between water pressure and velocity was established by hicai and Bunny: the theoretical velocity at the end of the pipe completely changed with the size of its hydrostatic head without friction loss.
The above research has laid the foundation for the development of water meters.
The world's first water meter
In 1825, British samillo cross invented the balance tank water meter and obtained the first patent. The water meter has two tanks with equal volume and a rotating shaft in the middle, so that the two tanks are in balance. After water is injected into one of the tanks from top to bottom, it will sag automatically and pour out the water due to the increase of weight. At the same time, the other tank is moved to the water receiving position, so that the reciprocating operation can continuously measure the flow of water.
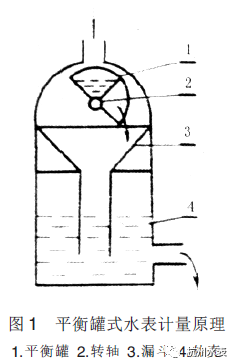
▲ in 1825, samillo cross, an Englishman, invented the balance tank water meter
The advent of the first positive displacement single piston water meter
In 1852, the British Thomas Kennedy invented the positive displacement single piston water meter. A piston B with a rubber ring is installed in the vertical metering cylinder a of the water meter, the rack f on the piston D is meshed with the gear e, and one end of the gear e shaft is connected with the clutch g to drive the metering indicator. When the measured water passes through the water inlet end of the two position four-way cock C, it flows into the upper and lower parts of the metering cylinder alternately to push the piston to move back and forth up and down. When the piston reaches the top of the upper part or the top of the lower part of the metering cylinder, the four-way cock will change direction immediately. At the same time, the rack and pinion on the piston rod drives the clutch to rotate the axial direction of the metering indicator in one direction to indicate the water flow. Because the essence of this kind of water meter is to measure the volume of the actual fluid passing through the water meter. Therefore, the water meter adopting this principle is also called positive displacement water meter.
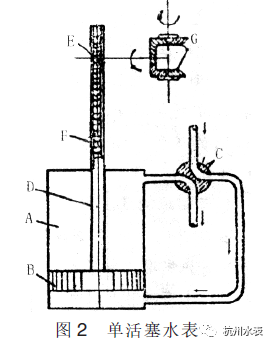
▲ in 1852, the Englishman Thomas Kennedy invented the single piston water meter
Volumetric water meter is popular for its accurate measurement and reliable operation. However, positive displacement water meters have high requirements for water quality. Due to the generally hard water quality in China, scale is easy to block, damage and reduce the accuracy of water meters. This foreshadows the emergence of the speed water meter widely used in domestic industrial and domestic water.
From positive displacement water meter to speed water meter
In national standards, "Speed water meter" is defined as "a water meter installed in a closed pipe, composed of a power element and directly moved by the water flow speed". When the water flows through the water meter, the impeller (rotor or spiral wing) is driven Rotation, and the flow velocity of the water flow is directly proportional to the speed of the impeller. Because the cross-sectional area of the nozzle at the water flow driving the impeller is constant, the speed of the impeller is also directly proportional to the flow. The linkage part on the impeller shaft is connected with the counting mechanism to make the counting mechanism accumulate the revolutions of the impeller (rotor or spiral wing), so as to record the amount of water passing through the water meter.
Typical speed water meters include rotor water meter, screw wing water meter, etc.
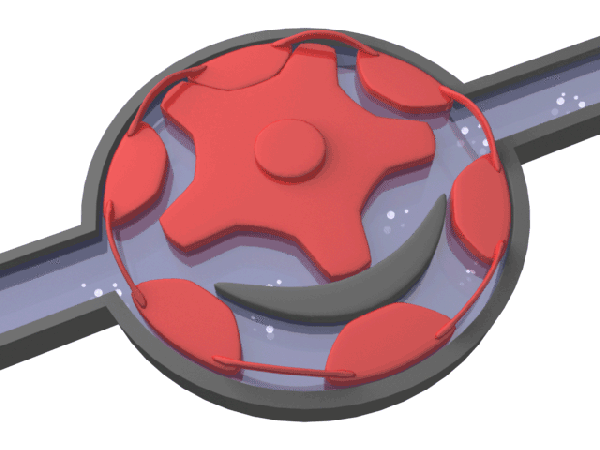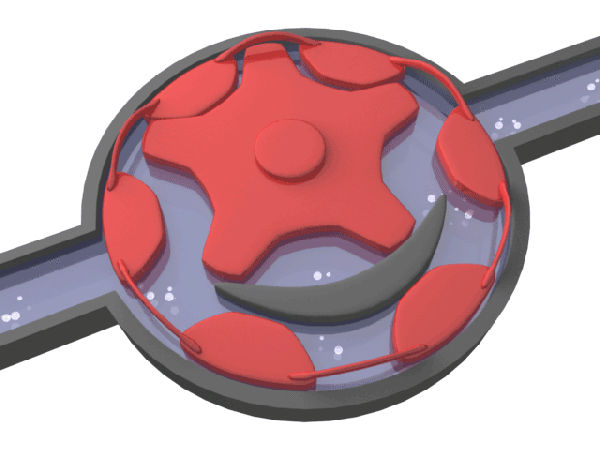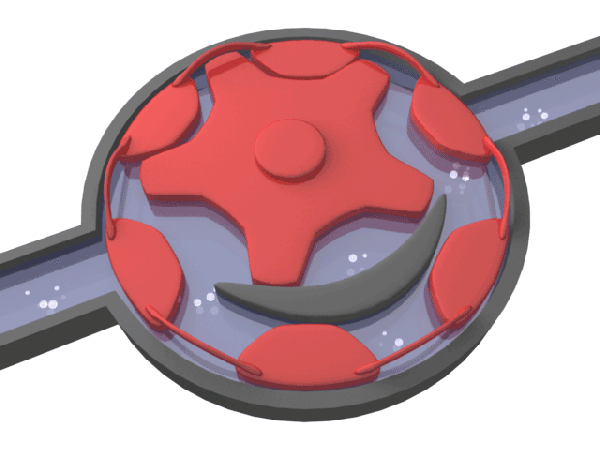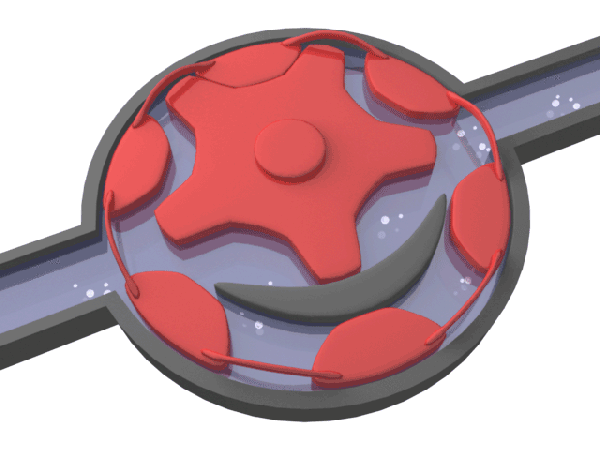
▲ typical speed water meter - schematic diagram of rotor water meter
The traditional mechanical water meters (speed and volume water meters) are gradually unable to meet the measurement needs due to the limitations of their measurement repeatability, service life and high requirements for water quality, as well as the difficulties in adjusting the flow measurement characteristics, the inability of two-way measurement and the limited space for improving the measurement accuracy. Therefore, a new generation of electronic water meters came into being.
A new generation of water meter electronic water meter
1. Electromagnetic water meter
The basic principle of electromagnetic water meter is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. When the conductive liquid medium (such as drinking water) flows through the non-conductive magnet measuring tube and cuts the magnetic line of force generated by the excitation magnetic field, the conductive liquid medium will generate the induced electromotive force. The induced electromotive force can be led out by placing it on a pair of electrodes perpendicular to the magnetic line of force and the measuring tube. Since the induced electromotive force is directly proportional to the intensity of the excitation magnetic field and the average flow rate of the medium, the flow rate of the measured medium can be measured from the strength of the induced electromotive force.
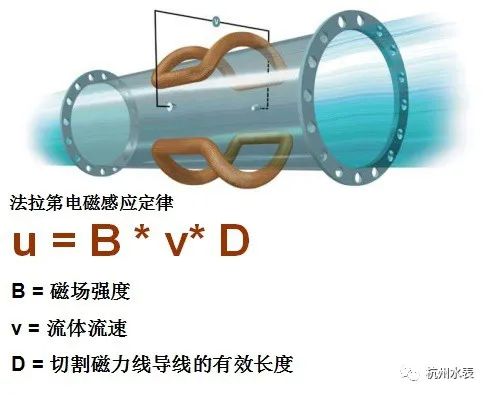
▲ working principle diagram of electromagnetic water meter
2. Ultrasonic water meter
Different from the electromagnetic water meter, the principle of ultrasonic water meter is that when the sound wave propagation direction is the same as the fluid flow direction (from point a to point B), its propagation time is less than that of countercurrent (from point B to point a). The difference in sound transmission time can reflect the flow rate in the pipeline. Ultrasonic water meter is usually composed of ultrasonic transducer and measuring tube. With the support of signal processing module and related algorithms, it can accurately measure the flow characteristics of water in pipeline.

▲ common measurement principles of ultrasonic water meter (taking time difference method as an example)
Today, the domestic water meter industry has entered a situation where two generations of water meters coexist. However, as people have higher and higher requirements for the performance, reliability, accuracy and adaptability of water meters, the market share of electronic water meters representing the future is rising year by year.